EDITORIAL
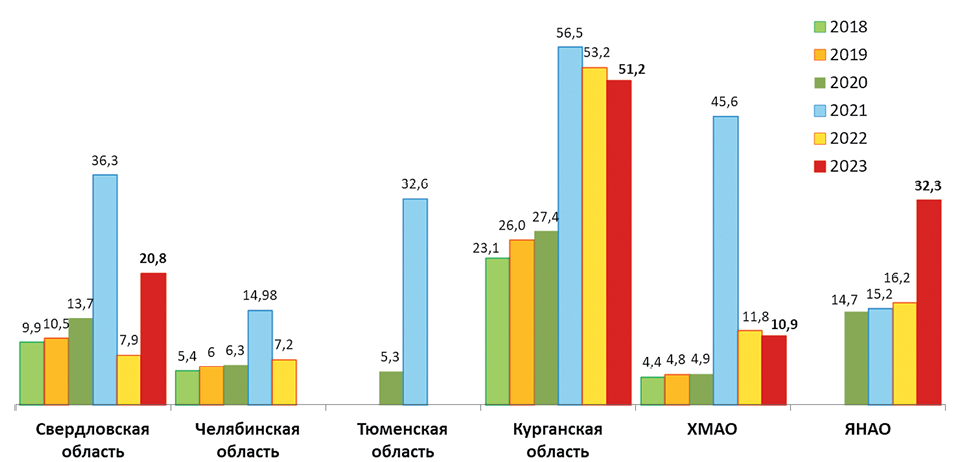
The article provides analytical data on the results of the obstetrics and childhood service of the Ural Federal District in 2023, analyzes the key indicators of the service over the past five years and provides directions for optimizing the work of the service. In the sphere of implementation of national projects “Healthcare” and “Demography”, applied scientific research and development of the “Ural Research Institute of Maternity and Child Care” of the Russian Ministry of Health makes a significant contribution to the development of medicine by improving methods of prediction, diagnosis, treatment and prevention of perinatal pathology, development of assisted reproductive technologies, which will improve the work of obstetrics and childhood services.
REVIEWS
The purpose of this literature review is to analyze the results of fetoscopic laser photocoagulation of placental anastomoses, obtained in various studies published in foreign and domestic medical publications in recent years.
Materials and methods. The review included published data over the last 10 years. The literature search was conducted in Medline, Scopus, Web of Science, Google Scholar, PubMed, Wiley and Cochrane Library databases.
Result. As a result of the analysis, the main ultrasound and fetoscopic markers influencing the outcome of the surgical treatment were determined: the location of the placenta on the anterior and posterior walls, the location of the umbilical cord attachment, the number of placental anastomoses; abnormal graphs of blood flow rates in the umbilical cord arteries; the distance between the attachment points of the umbilical cord; dissociated growth of the fetuses; the duration of gestation and the stage of severity of twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome, as measured with the R. Quintero staging system, at the time of the operation; the experience of the operating surgeons; and the duration of the operation.
Conclusion. Analysis of the literature data has shown that these markers are extremely unreliable in predicting the chances of survival for one or both fetuses. Further study of ultra-sound and fetoscopy predictors of adverse outcome of laser photocoagulation of placental anastomoses will allow for a more balanced approach to the choice of surgical tactics and personalized consultations with patients.
Background. Diseases of the endocrine system in their mothers, namely gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), have a significant impact on the increase in morbidity in newborns. The main adverse outcome for children of mothers with GDM is macrosomia, as prenatal exposure to hyperglycemia increases the risk and programs the offspring to develop diabetes and/ or obesity in adulthood.
Objective. To summarize modern scientific ideas about the impact of GDM on immediate and long-term disorders of health and lipid metabolism in newborns and young children.
Material and methods. An extensive literature review was conducted using the MEDLINE database (PubMed) using keywords and filter: randomized controlled trial, meta-analysis, systematic review.
Research results. This review summarizes the main evidence on the impact of maternal hyperglycemia on the health of her child and provides new information on the role of GDM in lipid disorders in newborns and young children.
Conclusion. Children born to mothers with GDM have an increased risk of developing obesity and impaired glucose tolerance from a very early age and throughout all periods of child-hood. Maternal hyperglycemia affects both during pregnancy and the rate of physical development of children in early life. These studies are important given that neonatal fat, rather than birth weight, is an important risk factor for the development of obesity later in life.to summarize modern scientific ideas about the effect of GDM on immediate and long-term disorders of health and lipid metabolism in newborns and young children.
Background. The success of assisted reproductive technologies depends on many factors, the main ones being the quality and genetic status of the embryo and endometrial receptivity. Preimplantation genetic testing is a tool that aims to reduce the risk of selecting an aneuploid embryo for transfer. Disputes surrounding the use of preimplantation genetic testing are conducted in the context of older patients, with recurrent miscarriage, with genetic karyotype abnormalities in a married couple, as well as multiple unsuccessful attempts at ART in the anamnesis.
Purpose of review. To summarize and analyze the available data on current trends in the use of preimplantation genetic testing (PGT-A).
Materials and methods. The review includes published data over the past 10 years regarding the effectiveness of ART programs and pregnancy outcomes after the use of preimplantation genetic testing. The literature search was conducted in Medline, Scopus, Web of Science, Google Scholar, PubMed, Wiley and Cochrane Library databases.
Results. According to most authors, preimplantation genetic testing does not improve live birth rates per patient in the general population, but it does improve live birth rates when performing PGT-A on blastocyst-stage embryos in women over 35 years of age, as well as in women with a history of pregnancy loss to reduce risk miscarriage of a subsequent pregnancy.
Conclusion. Preimplantation genetic testing is a valid method for assessing euploidy and mosaicism of an embryo before transfer. The feasibility of use, according to research results, is more related to conditions in which the risk of embryonic aneuploidy may increase, and is justified in high-risk patients, while the use of this technique in patients with a good prognosis is still questionable. First, trophectoderm biopsies may not reflect the ploidy of the inner cell mass. Secondly, even if we assume that this is the case, we cannot be sure that the embryonic cell line will not self-correct. In other words, once a diagnosis of PGT-A is received suggesting mosaicism or aneuploidy, the likelihood of a false-positive diagnosis is high.
Background. Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) is an incretin hormone whose mechanism of action also includes a slight delay in gastric emptying (GE). Due to the prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity, GLP-1drugs are prescribed to many patients, including women of reproductive age who are also taking COCs. For oral contraceptives, malabsorption may result in ineffective pregnancy prevention.
The purpose of this literature review was to review data from studies on the effect of GLP-1 agonists on oral hormonal contraceptives (COCs) and to analyze data on the safety of concomitant use of COCs and GLP-1 agonists.
Methods. PubMed and ClinicalTrials.gov were searched for publications using keywords. A total of 3 clinical studies were selected for inclusion in the literature review.
Results. Studies involving GLP-1 have not revealed a statistically or clinically significant difference in drug-drug interactions with COC drugs.
Conclusion. This review compared the effects of currently available GLP-1 on COCs in three clinical studies. Due to the prevalence of type 2 diabetes and obesity, GLP-1 is likely to be prescribed to many patients, including women of reproductive age who are also taking COCs. These drugs may affect the pharmacokinetics of COCs. Changes in the area under the curve, maximum concentration, and time to maximum plasma concentration of oral drugs can be avoided by taking these drugs 1 hour after GLP-1.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Introduction. Fetal echocardiography is currently one of the main methods of prenatal diagnosis. However, in recent years, attention has shifted towards the use of ultrasound to assess fetal myocardial function.
The aim of this study is compare global longitudinal deformation of the myocardium of the left (LV) and right ventricles (RV) of the heart in fetuses with uncomplicated singleton pregnancy, in fetuses from monochorionic twins with transfusion syndrome, selective growth retardation and in uncomplicated monochorionic multiple pregnancy.
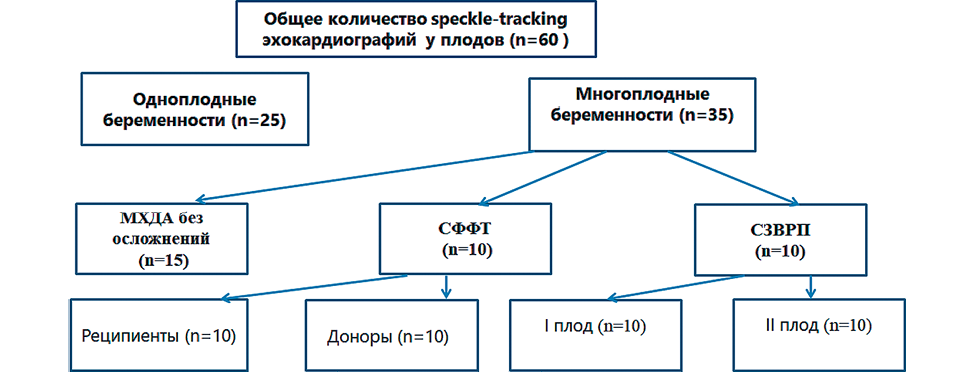
Material and methods. A prospective cohort study was conducted which included 60 pregnant patients: Group I — patients with an uncomplicated singleton pregnancy (n=25); Group II — 35 patients with monochorionic diamniotic twins, whose pregnancy in 10 cases was complicated by feto-fetal transfusion syndrome (stages I-III according to Quintero R.A.), in 10 cases — selective growth retardation of the second fetus and in 15 cases monochorionic twins without complications. The following parameters were determined: global longitudinal deformation (GLD) of the myocardium of the ventricles of fetal hearts using the speckle tracking method of ejection fraction (EF), end-diastolic and end-systolic volumes of the ventricles of the heart.
Results. Significant differences were established in GLD of RV and LV between singleton and monochorionic multiple pregnancies (LV: -21.2 ± 2.03 versus -23.41 ± 0 .25, p = 0.003); RV: — 20.3 ± 2.5 versus -23.3 ± 2.5, p = 0.013). Significant differences were revealed in GLD of the LV and RV in recipient fetuses before and after laser coagulation of placental anastomoses (LPCA) [LV in recipients before LCPA (- 20.4 ± 2.98) versus LV recipient after LCPA (-24.2 ± 3.3), p = 0.018], [RV in recipients before LKPA (- 20.4 ± 2.8) vs. RV in recipients after laser coagulation of placental anastomoses (-23.7 ± 3.4, p = 0.012].
Conclusion. Assessment of the cardiac function of fetuses from monochorionic twins using the echocardiographic speckle tracking technique makes it possible to identify early changes in fetal myocardial function in twins from monochorionic diamniotic twins, as well as to carry out reliable testing monitoring changes in cardiac function over time.
Background. There is a lot of data in the literature showing the state of the hemostatic system and endothelium separately in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) and placental insufficiency (PI). However, with the combination of the above complications of pregnancy, there is very little research, therefore, the problem requires detailed study.
Objective. To determine the contribution of the functional state of the endothelium and the hemocoagulation system to the formation of placental insufficiency in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus without insulin requirement.
Materials and methods. A longitudinal cohort comparative study was conducted. The study included 120 patients in the II-III trimester of pregnancy with GDM without insulin requirement. The main group consisted of 70 women whose pregnancy was complicated by sub- and decompensated forms of PN. The comparison group included 50 pregnant women without pathology of the fetoplacental complex. The hemostasis system was studied using clotting tests and thromboelastometry. The concentrations of VEGF-A, total nitrite (NO2 total), endogenous nitrite (NO2 endogenous), nitric oxide (NO) in peripheral blood were determined by ELISA. Comparison of continuous quantitative data was carried out using the Mann-Whitney test, which was calculated using the MedCalc 15.8 application program. The null hypothesis was rejected at p<0.05.
Result. The value of the integral index of coagulation, onset time and initial speed of clot formation in the main group was statistically significantly higher than in patients in the comparison group, p<0.05. The level of VEGF-A in pregnant women of the main group was statistically significantly lower than that in the comparison group, p<0.05. The indicator of total NO2 and NO in the main group was statistically significantly lower than in the comparison group, p<0.05. The endogenous NO2 indicator did not differ statistically significantly between groups.
Conclusion. In patients with GDM on diet therapy and PN, endothelial dysfunction and, as a consequence, hypercoagulation occur.
Background. Endometriosis is a chronic multifactorial disease that affects more than 170 million women of reproductive age worldwide, causing pelvic pain syndrome, dyspareunia, and symptoms of gastrointestinal dyspepsia, thereby having a negative impact on the psycho-emotional state of patients. Despite a wide range of medical and surgical treatments, the relapse rate reaches 50%, which is a global economic and social problem.
The purpose of the study. To determine the spectrum of clinical features of the gastrointestinal tract in women with recurrent deep infiltrative endometriosis.
Materials and methods. The study included 113 patients of reproductive age who underwent surgical treatment of common forms of external genital endometriosis. The main group consisted of 32 patients who underwent repeated surgical treatment due to relapse of deep infiltrative endometriosis, the comparison group — 51 patients without relapse of the disease one year after the primary operation, the control group — 30 patients of reproductive age who did not suffer from external genital endometriosis. An analysis of the somatic anamnesis was carried out, as well as questionnaire data on pelvic pain on a visual analogue scale (VAS) and functional bowel disorders in patients with deep infiltrating endometriosis, depending on the status of relapse of the disease.
Results and discussion. Patients of the main group suffered significantly more often from functional diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (71.9% (23/32) versus 51.3% (26/51) in the comparison group; p = 0.006, the spectrum of which was represented by chronic gastritis and irritable bowel syndrome. In the main group, the clinical manifestations of gastrointestinal dyspepsia before surgical treatment correspond to a moderately severe degree of 17.706 (4.601) points. A significantly higher initial level of functional intestinal disorders was established during subjective assessment in the main observation group: 17.706 (4.601) points versus 10.66 (3.61) points in the comparison group; p=0.001. In women of the main observation group, one month after surgical treatment, there was a significant decrease in subjective assessment of the severity of functional intestinal disorders (from 17.71 (4.60) points to 9.86 (4.73) points; p = 0.001). The integral VAS pain score in the main group was 6.65 (1.53) points, which is significantly higher than in patients in the comparison group without relapse of the disease.
Conclusions. The identified clinical and anamnestic predictors of the recurrent course of deep infiltrative endometriosis will allow us to formulate a personalized approach at the pre- and postoperative stage, aimed at preventing relapse of the disease, which will directly improve the psycho-emotional state and quality of life of women.
Background. In modern literature, there is a limited number of publications devoted to the characteristics of the course of endometriosis in patients with cervical diseases (CD), the choice of management tactics for cervical diseases and the prevention of relapses of these diseases.
Objective. To analyze clinical, anamnestic and laboratory data in patients of reproductive age with a combination of benign cervical diseases and external genital endometriosis.
Materials and methods. A retrospective cohort study was conducted that included 100 women of reproductive age with external genital endometriosis. The main group consisted of 56 patients with a combination of benign cervical diseases and external genital endometriosis. The comparison group consisted of 44 patients with external genital endometriosis without cervical cancer. An assessment was made of clinical and anamnestic data, the results of a cytological examination of a cervical smear, extended colposcopy and the level of hormones AMH, FSH, estradiol, performed by enzyme immunoassay on days 2-5 of the menstrual cycle. Statistical analysis was carried out using the SPSS Statistics 26.0 program.
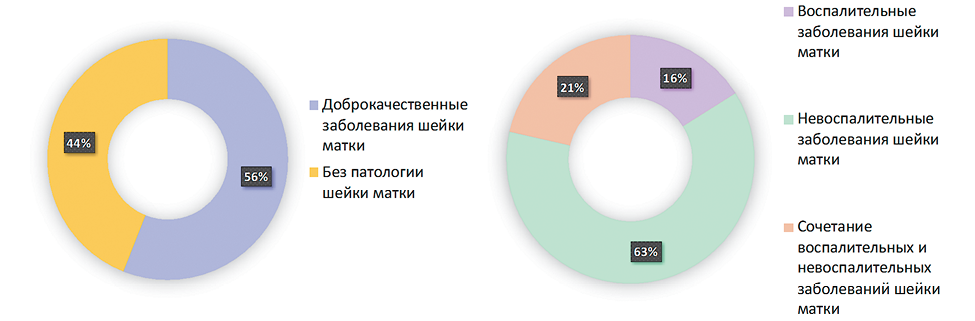
Results. External genital endometriosis in 56% of cases is associated with benign cervical diseases, in the structure of which non-inflammatory diseases predominate (63%). Inflammatory diseases of the cervix were observed in 16% of patients, and combined pathology of the cervix was observed in 21% of women with external genital endometriosis. The presence of concomitant cervical pathology in 83.3% of cases is accompanied by endometriosis-associated infertility, this is significantly more common than in patients with inflammatory (22.2%) and non-inflammatory (42.9%) cervical diseases, p < 0.05. Surgical treatment of endometriosis did not lead to pregnancy within one year after surgery in any planning patient with concomitant cervical pathology (0/11); this figure in women with non-inflammatory cervical diseases was 14.3% (4/32), whereas in 75.0% (3/4) with inflammatory diseases of the cervix, pregnancy occurred within a year after surgery, p<0.05. In turn, the presence of inflammatory cervical diseases was associated with a significantly lower level of AMH (1.4±0.5 ng/ml) compared to patients with non-inflammatory cervical diseases (3.0±0.4 ng/ml) and combined cervical cancer pathology (3.4±0.5 ng/ml), p<0.017. A significant decrease in ovarian reserve in the future can also lead to impaired fertility in this category of patients.
Conclusion. The results of the study indicate the need for a comprehensive assessment of the condition of the cervix in patients with genital endometriosis, including a thorough history taking, cytological examination and extended colposcopy in combination with determination of HPV virus carriage. Timely measures for the diagnosis and treatment of cervical diseases in patients with endometriosis-associated infertility will improve fertility rates in this category of patients.
Background. The “poor” response to ovarian stimulation during IVF (in vitro fertilization) cycles depends on various factors, including the biochemical composition of the follicle microenvironment. Recent studies have focused on the relationship between vascular tone regulators, angiogenic factors, oxidative stress, and the quality of oocytes. Despite this, there is still no consensus on the exact effect of these factors on folliculogenesis or their role in “poor” responses.
Objective. To evaluate the content of biochemical factors and regulators of vascular tone and angiogenesis in follicular fluid in patients with a “poor” ovarian response to stimulation in IVF programs, compared to similar indicators in women with a normal ovarian response.
Materials and methods. An open prospective cohort study was conducted, including 56 patients who were part of the IVF program. The criterion for separating the cohort of women was their response to controlled ovarian stimulation during the IVF cycle. Women with a “poor” response (n=32) were placed in the main group, while those with a normal response (n=24) were in the comparison group. Follicular fluid samples from women with a “poor” response were divided into two subgroups based on the presence or absence of an oocyte-cumulus complex in the follicle. The biochemical and soluble regulatory factors in follicular fluid were analyzed in both groups after controlled ovarian stimulation was completed. Statistical analysis of the data was done using methods from variation statistics. A critical level of significance for the differences was set at p ≤0.05.
Result. The levels of urea, glucose, high-density lipoprotein, and total antioxidant status (TAOS) in follicular fluid (FF) from patients with a “poor” ovarian response were statistically significantly higher compared to those in the control group. The levels of bilirubin, low-density lipoprotein, and uric acid were also significantly lower in VF from patients in the main group compared to the control group, p<0.05. The indices of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF-A) and vascular endothelial growth receptor-2 (VEGFR-2) in FF from women with a “poor” response were significantly lower than those from patients with a normal response, while the levels of endogenous nitric oxide were significantly higher in the former group compared to the latter, p<0.05.
Conclusion. The absence of an oocyte-cumulus complex in the pre-ovulatory follicle, which is associated with a “poor” response of the ovary to stimulation, is likely due to a disruption in vascularization processes. This is supported by a decrease in the levels of pro- and anti-angiogenic factors, such as VEGF-A and VEGFR-2.
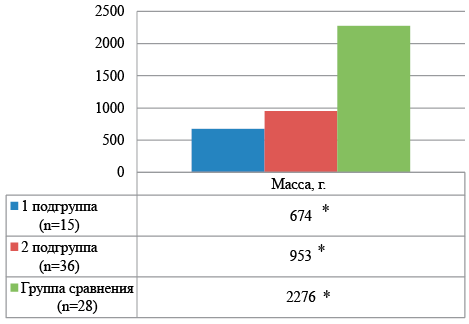
Background. Children born at extremely early preterm birth (EPL) are at high risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, including heart rhythm disorders (HRDs) and conduction disorders throughout life.
Objective: To study electrocardiographic features in children of the first year of life born at term SPR.
Materials and methods. The main group consisted of 51 children born at term. Depending on body weight, the main group was divided into 2 subgroups. Subgroup 1 consisted of children weighing 500-750 g (n=15). Subgroup 2 — children weighing 751 g or more (n=36). The comparison group included 28 children born at a gestational age of 32-36 weeks. Children were examined at the ages of 6 and 12 months. Electrocardiography was performed on children at rest in 12 standard leads with a paper tape speed of 50 mm/sec. Analysis of ECG indicators was carried out using a Sicard electrocardiograph from Siemens AG, according to generally accepted methods.
Results and discussion. In children born at gestational age during 1 year of life, clinical manifestations of impaired functional state of the cardiovascular system were observed in the form of vegetative-vascular dysfunction, NSR, and changes in the characteristics of heart sounds. According to the ECG results, NSR was identified in the form of sinus arrhythmia, sinus tachy- and bradycardia, extrasystole, atrial rhythm, pacemaker migration, supraventricular paroxysmal tachycardia, WPW syndrome, long QT interval syndrome, which amounted to 86.7% of cases in children of subgroup 1, in children of the 2nd subgroup 82.2% and 60.7% in children of the comparison group. A direct strong correlation has been established between the clinical manifestations of autonomic dysfunctions at the age of 12 months and the frequency of identified dysfunctions. By 12 months of life, the number of children with sinus bradycardia, sinus arrhythmia and ectopic rhythm increases. There is no positive trend in the frequency of detection of ECG phenomena during the first year of life.
Conclusion. Children born at very early preterm birth require cardiac monitoring, including blood pressure measurement, electrocardiography and the development of personalized clinical follow-up programs.
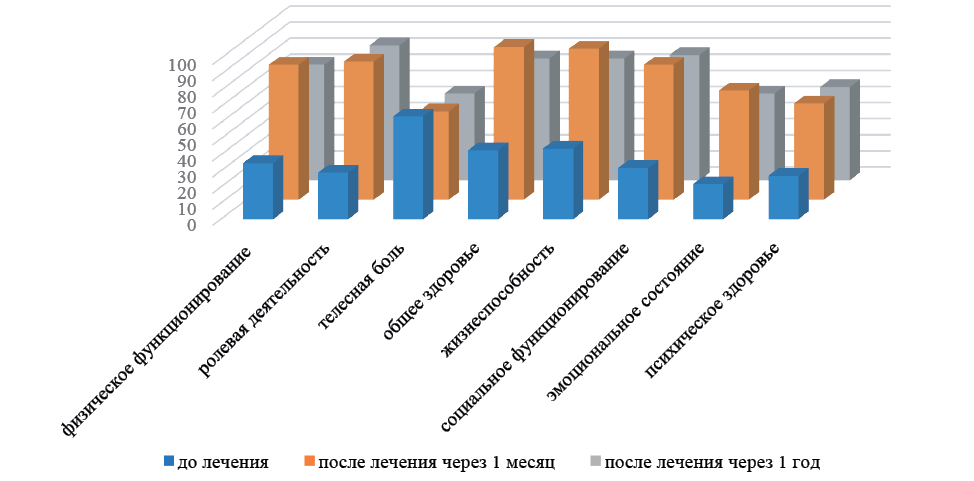
Background. With all the variety of treatment methods for pelvic organ prolapse (POP), the criteria for cure are reduced to the absence of anatomical defects of the pelvic floor. At the same time, the complete restoration of the physical, psycho-emotional and social components of a woman’s life is practically not taken into account. Studying the quality of life, as well as the sexual function of patients with POP will help to clarify the effectiveness of the synergy of surgical treatment and hardware rehabilitation methods.
The purpose of the study is to assess the quality of life and sexual function of women of reproductive age after reconstructive plastic surgery on the pelvic floor in combination with radiofrequency exposure.
Material and methods. An open prospective longitudinal study was conducted on 60 patients of reproductive age with stage II-III genital prolapse according to the POP-Q classification. The women were divided into two groups: group 1 — patients who underwent vaginal plastic surgery with their own tissues (n=30); group 2 — patients who, after reconstructive plastic interventions, underwent postoperative rehabilitation using dynamic quadripolar radiofrequency (n=30). Before surgery, 1 month and 1 year after treatment, a survey was conducted to determine the quality of life using the Short Form-36 questionnaire and sexual function using the Female Sexual Function Index and Female Sexual Distress Scale.
Research results. The combination of surgical correction of pelvic organ prolapse with subsequent radio wave therapy makes it possible to correct anatomical defects, and at the same time statistically significantly increases the index of quality of life and female sexual function, reducing a woman’s experiences associated with problems in her sexual life.
Conclusion. The synergy of surgical methods of correction and postoperative rehabilitation with the use of DCRF contributes to the long-term preservation of the functional results of treatment of pelvic floor incompetence during reproductive age.
Background. Pelvic organ prolapse is a common pathology that has a significant impact on women’s quality of life. According to literature data, 30% of women of reproductive age have symptomatic forms of pelvic organ prolapse (POP). 13% of patients undergo surgical treatment of POP. However, some patients again complain about the symptoms of genital prolapse, despite the surgical correction.
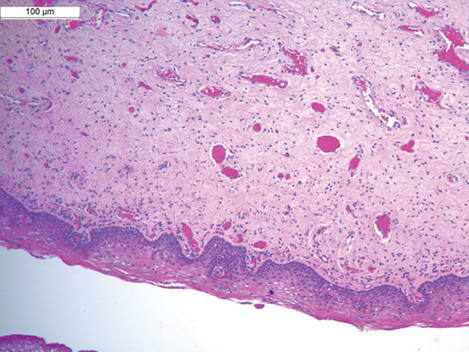
Objective. To evaluate the effect of dynamic quadripolar radio frequency on the histological picture of the vaginal mucosa in patients of reproductive age with pelvic organ prolapse.
Materials and methods. A prospective comparative study was conducted, which included 38 patients of reproductive age. The patients were randomized and divided into 2 groups 2 months before the surgical treatment of POP. The first group (n=17) of patients underwent preoperative preparation using dynamic quadripolar radio frequency (DQRF) before surgical treatment. The second group (n=21) did not undergo preoperative preparation. Both groups of women received surgical treatment in volume — plastic surgery of genital prolapse with their own tissues. A biopsy of the vaginal mucosa was obtained intraoperatively, and its histological assessment was performed. The material was stained with hematoxylin-eosin, light microscopy was performed using an Axioplan 2 microscope (CarlZeissJena, Germany).
Results. Increased vascularization of the vaginal mucosa, absence of signs of inflammation and fibrosis, and ordering of collagen bundles were noted in patients who underwent preoperative preparation using DQRF.
Conclusion. Changes in the histological picture of the vaginal mucosa after the use of DQRF indicate an increased regenerative ability of tissues, which may be a predictor of better healing after surgical treatment and may affect the long-term results of surgical treatment.
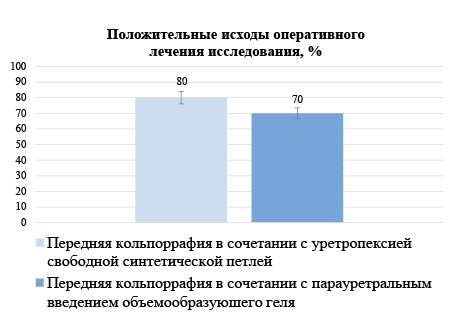
Background. The relevance of the problem of stress urinary incontinence (SUI) in combination with cystocele has increased significantly over the past decades, due to the high prevalence of the disease in the population, as well as increased awareness of patients about treatment options. It is known that one-stage surgical treatment significantly reduces the need for re-intervention and, accordingly, the rehabilitation period. The identification of significant criteria that are decisive in the effectiveness of various methods of surgical correction of SUI in combination with cystocele dictates the need for further research in this direction.
The purpose of the study. To determine outcome criteria for surgical treatment of stress urinary incontinence in combination with cystocele in postmenopausal women based on a comprehensive preoperative examination.
Materials and methods. A prospective randomized study was conducted, which included 80 women with stress urinary incontinence in combination with postmenopausal cystocele, who were routinely hospitalized in the gynecological department of the Federal State Budgetary Institution Research Institute of OMM for surgical treatment. All patients, after signing voluntary informed consent to participate in the study and conducting a comprehensive preoperative examination using a random number generator, were randomized into two groups of equal size. The first group included 40 women who received surgical treatment including anterior colporrhaphy in combination with urethropexy with a synthetic loop; the second group consisted of 40 patients who underwent surgical treatment using the method of paraurethral injection of a volume-forming gel in combination with anterior colporrhaphy.
Results and discussion. Criteria for predicting the outcome of surgical treatment of stress urinary incontinence in combination with cystocele in postmenopausal women were determined based on a comprehensive preoperative examination. Conclusion: Analysis of complex urodynamic and ultrasound examination methods in women revealed statistically significant differences between groups of women with positive and negative outcomes of surgical treatment. The identified criteria for predicting the outcome of surgical treatment serve to assist the clinician in choosing the optimal, most effective method of treating SUI in combination with cystocele in postmenopausal women.
Conclusions. Analysis of complex urodynamic and ultrasound methods of examination in women revealed statistically significant differences between groups of women with positive and negative outcomes of surgical treatment. The identified criteria for predicting the out-come of surgical treatment serve to assist the clinician in choosing the optimal, most effective method of treating SUI in combination with cystocele in postmenopausal women.