EDITORIAL
Introduction. Endometriosis is a chronic, hormone-dependent, slowly progressive disease that affects up to 190 million (10 %) women worldwide. Current literature lacks data on the characteristics of endometriosis in patients with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, as well as on the choice of treatment strategies and recurrence prevention for these diseases.
Study Objective. To evaluate the interaction between clinical and anamnestic data, vaginal microbiota status, and HPV infection in patients with deep endometriosis and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia.
Materials and methods. A prospective comparative study was conducted on 103 patients of reproductive age who underwent surgical treatment for common forms of external genital endometriosis. These included 52 patients with deep endometriosis combined with grade 1 cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (the study group) and 51 patients with deep endometriosis without cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (the comparison group).A medical history was analyzed. Vaginal microbiota composition and HPV typing were assessed using real-time quantitative PCR.
Results. When assessing the nature of concomitant somatic pathology, it was found that patients in the main group significantly more often suffered from alimentary obesity 1/52 (40.4 %) versus 8/51 (15.7 %) in the comparison group, p = 0.010, gastrointestinal diseases 1/52 (20.4 %) versus 4/51 (7.8 %), p < 0.001, diseases of the urinary system in 23/52 (44.2 %), versus 6/51 11.8 %, p = 0.001, skin diseases of viral etiology in 16/52 (30.8 %) versus 1/51 (2.0 %), p < 0.001. When comparing the correlations between opportunistic microorganisms in the vaginal microbiota and clinical and anamnestic parameters in patients with deep endometriosis and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, strong and moderate correlations were found between the prevalence of the complex of opportunistic microorganisms Gardnerella vaginalis + Prevotella bivia + Porphyromonas spp. in the vaginal microbiota and the presence of chronic cystitis (r = 0.555894), sexually transmitted infections (r = 0.452654), and recurrent endometriosis (r = 0.504666);Strong positive correlations were found between highly carcinogenic virus types: HPV type 16 and a history of chronic endometritis (r = 0.401496); Between HPV type 31 and chronic cystitis (r = 0.532417), as well as a history of bacterial vaginosis (r = 0.545374); between HPV type 35 and a history of sexually transmitted infections (r=0.514113); between HPV type 45 and recurrent endometriosis (r = 0.56018), as well as a history of ovarian endometriectomy
(r=0.468031); between HPV type 53 and a history of hemorrhoids (r = 0.514113). Strong correlations were established between patients with 2 or more HPV types and the presence of chronic cystitis (r = 0.620546).
Conclusion. The course of external genital endometriosis in combination with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia may represent a single pathological process involving the interaction and mutual influence of various factors within the host and microbiota, which determine the phenotype of polyproliferative pathology in women of reproductive age.
REVIEWS
Introduction. To date, there is no unified classification or standardized protocols for the diagnosis and treatment of uterine infertility. This is due to the heterogeneity of its causes, as well as insufficient awareness of modern methods for assessing endometrial receptivity.
Objective. To conduct a comprehensive analysis of new methods for diagnosing hypoplastic endometrium, as well as to evaluate modern approaches aimed at restoring endometrial receptive potential in women with uterine infertility.
Materials and Methods. The review includes published data from the past 10 years. A literature search was conducted in the Medline, Scopus, Web of Science, Google Scholar, PubMed, Wiley, and Cochrane Library databases. Data from 54 foreign and domestic sources were analyzed.
Results. Implantation failure associated with uterine factor infertility reduces the likelihood of natural attachment of a fertilized egg to the endometrium, which becomes a serious barrier to spontaneous conception and successful pregnancy. A fundamental factor in this process is endometrial atrophy, one of the key causes of infertility according to reproductive disorders statistics. Diagnosis of endometrial condition is critical for successful pregnancy planning in both natural cycles and ART programs, as even a high-quality embryo may fail to implant due to endometrial incompetence. Despite the accumulated experience in diagnosing and treating the problem of “thin” endometrium during the pre-pregnancy stage, this issue remains controversial and requires further scientific research.
Conclusion. Thus, achieving successful implantation and pregnancy in women with uterine infertility requires a comprehensive and multi-faceted examination to identify pathological changes in the endometrium that adversely affect its receptivity. Optimization of endometrial parameters is essential for improving reproductive outcomes and the effectiveness of assisted reproductive technology programs.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Introduction. With the expansion of single embryo transfer practices, selecting the most competent embryo is becoming critical for achieving high reproductive outcomes. Morphological assessment, including the Gardner classification, remains a widely used tool; however, its prognostic value remains limited and variable. Time-lapse imaging technology
allows for recording embryo morphokinetic parameters and developing implantation prediction algorithms based on the timing of key developmental stages. Research shows the influence of a number of factors — woman’s age, body weight, smoking, and endometriosis — on morphokinetic parameters. However, the advantages of TLM over traditional culture remain unclear. Nevertheless, the use of time-lapse imaging can improve the accuracy of embryo selection, including the selection of candidates for transfer or PGT-A, which is particularly important in patients of advanced reproductive age.
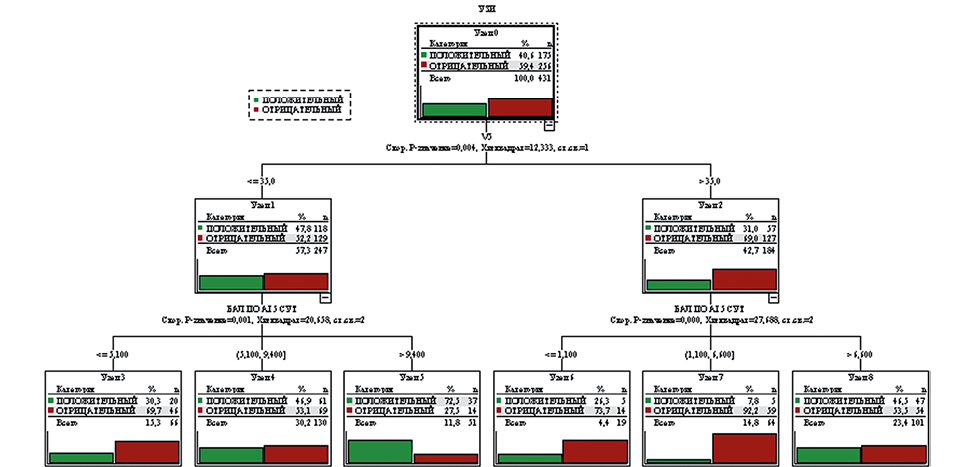
Objective. To identify prognostic factors for a positive IVF outcome based on classification tree analysis.
Materials and methods. Data from 431 IVF cycles were analyzed. A positive outcome was defined as clinical pregnancy, and a negative outcome was defined as its absence. The CHAID method was used to identify significant predictors. The analysis included patient age and morphokinetic parameters of embryo development by day 5 of culture.
Results. The key discriminatory factor was patient age (≤ 35 years) (p = 0.004). In this group, the success rate was 47.8 %, compared to 31.0 % in patients over 35 years of age. Among women ≤ 35 years of age, the most significant factor was the morphokinetic assessment score (AI score on day 5, p = 0.001): with a score > 9.4, the probability of a successful outcome reached 72.5 %, while with a score ≤ 5.1, it was only 30.3 %. A similar pattern persisted in patients over 35 years of age (p < 0.001), but the success rate with high scores decreased to 46.5 %.
Conclusion. Patient age and embryo morphokinetic assessment are independent predictors of IVF success. Using a classification tree allows for personalized outcome prognosis and optimized embryo transfer strategies.
Background. One of the most important indicators reflecting differences in the viability of an organism and determining the survival of a population is the sex ratio. This indicator is relatively stable for the entire human population and for individual regions. However, when performing ART, there is a certain risk of a change in the sex ratio at birth, which may be due to the peculiarities of technology and a number of other reasons. In this regard, the question
of whether there are differences in the gender ratio in the initial infertility in marriage, depending on the method of conception: spontaneous conception or the use of various ART technologies, is debatable.
The aim of the study was to determine the sex ratio of the fetus during pregnancy resulting from the use of assisted reproductive technologies (ART) in comparison with natural conception in couples with infertility.
Objective. To determine the sex ratio of the fetus during pregnancy resulting from the use of assisted reproductive technologies (ART) in comparison with natural conception in couples with infertility.
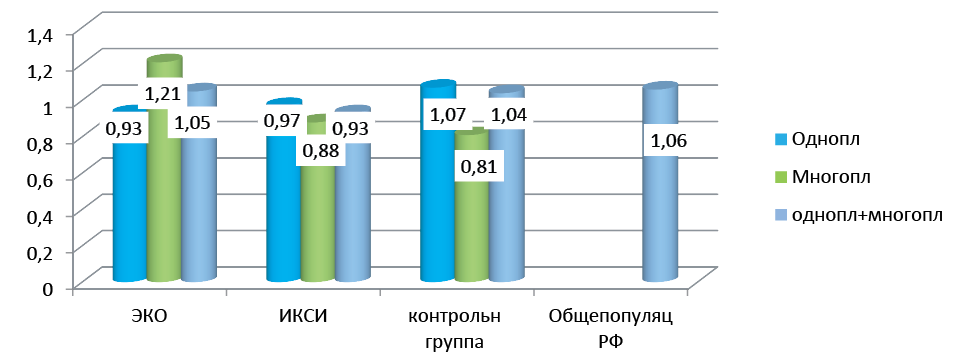
Materials and methods. The analysis of the secondary sex ratio in patients with overcome infertility using various ART technologies (IVF and ICSI) — the main group (N=1177) and spontaneous pregnancy — the comparison group (N=376), as well as the results of cytogenetic studies of abortive material of patients with undeveloped pregnancy after various ART technologies and spontaneous pregnancy.
Results. The conducted studies have shown that the secondary sex ratio in newborns does not have significant differences depending on the method of pregnancy (spontaneous or traditional IVF). However, in induced pregnancy using ICSI, there is a tendency to shift the ratio towards the female sex, which is due to increased death of embryos with a male karyotype in the early stages of pregnancy. Obviously, female embryos conceived with this technology are more viable if they have a normal karyotype.
Conclusion. The identified trends require further study for a more reliable assessment of differences in the viability of organisms of different sexes in different periods of ontogenesis during induced pregnancy using the ICSI procedure.
Summary. Chronic endometritis (CE) is a key problem in modern reproductive medicine. A complex of antimicrobial peptides and cytokines (AMPC), derived from pig mononuclear cells, exhibits pronounced anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and reparative effects, theoretically enabling simultaneous targeting of multiple pathways in CE pathogenesis.
The purpose of the study. Develop and evaluate the effectiveness of an innovative treatment strategy for chronic endometritis (CE) during the period of preparation for pregnancy to restore fertility.
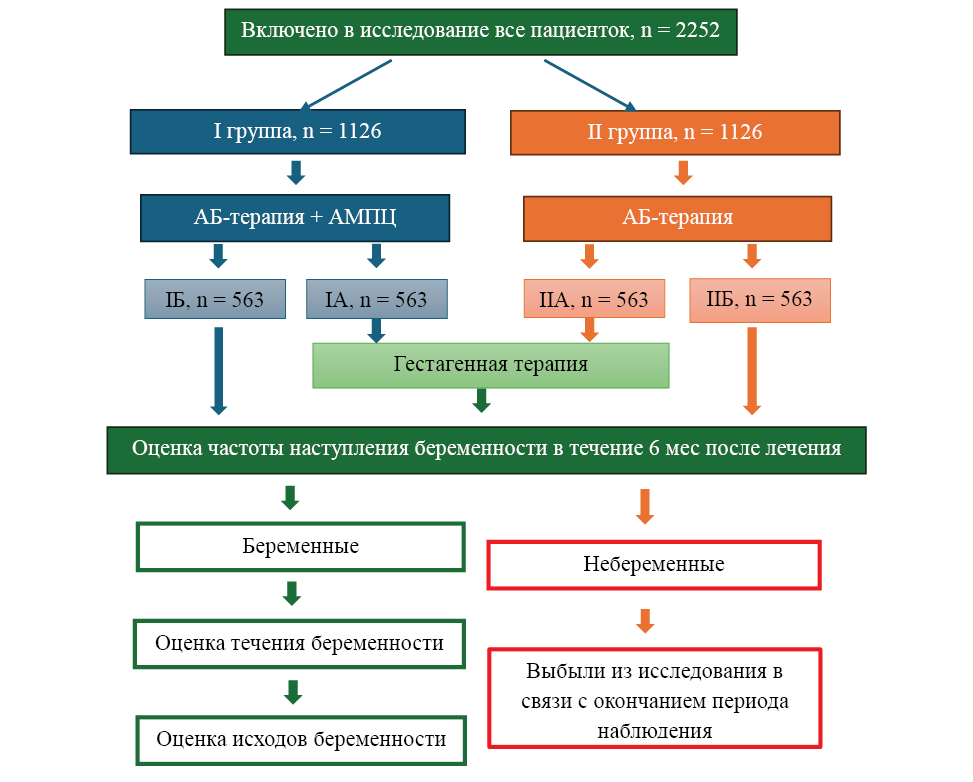
Materials and methods. A two-stage prospective randomized controlled parallel-group study was conducted. The study included 2,252 patients with uterine infertility and morphological signs of chronic endometritis, divided into two main cohorts: the first group (n = 1,126), receiving combined therapy: an antibacterial drug + an immunomodulator (a complex of antimicrobial peptides and cytokines — AMPС), was divided into subgroups A (additionally included progestogens with the combined therapy) and B (without progestogens). The second group received antibacterial therapy (AB) and was also divided into subgroups A and B: with progestogen support and without it. Endometrial recovery was assessed based on histological and immunohistochemical examination, as well as the rate of spontaneous pregnancy and live births in each group.
Results and discussion. The use of combination therapy with AMPT contributed to the resolution of HE in 85.3 % of patients compared with 60.3 % in the AB monotherapy group (p < 0.001). In the AMPT/AB/progestogen group, the frequency of spontaneous pregnancy reached 83.8 % versus 53.8 % in the AB/progestogen group (p < 0.001). Live births were significantly more frequent in the main group: 73.5 % versus 41.2 % (p < 0.001). When preparing for ART programmes, the use of AMPT increased the likelihood of pregnancy after cryotransfer by 1.5 times (83.8 % vs. 58.1 %) and live births by 2 times (72.1 % vs. 35.3 %). Two courses of AMPT demonstrated higher therapeutic efficacy. Based on neural network analysis, prognostic models were developed with an accuracy of 88.0 % for spontaneous pregnancy and 97.9 % for IVF outcomes.
Conclusion. The proposed comprehensive pathogenetic therapy of chronic endometritis (CE) including AMPС demonstrates high efficacy compared to the group receiving only antibiotic therapy and significantly increases the frequency of conception and live births both in natural cycles and in ART programs, which allows this method to be recommended for implementation in clinical practice.
Summary. Abnormal placental insertion is a cause of massive obstetric hemorrhage, maternal and perinatal morbidity, and mortality.
The pathogenesis of placenta accreta is currently unknown, and there are no definitive instrumental or serum tests for the precise diagnosis of placenta accreta spectrum (PAS), which underpins the relevance of this study.
The purpose of the study. To study placental expression of erythropoietin and ghrelin in pathological placental attachment.
Materials and methods. A morphological study of the placenta of women who gave birth in the inpatient department of the Clinic of the Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education South Ural State Medical University of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation in Chelyabinsk was conducted (53 specimens): group 1 — 21 specimens of normally located placentas, group 2 — 17 specimens of placenta previa without signs of placenta accreta, group 3 — 15 specimens of placenta previa (7 cases of placenta accreta, 5 — placenta increta, 3 — placenta percreta, invasion degree 3a). The expression of erythropoietin (EPO) and ghrelin in the placenta was studied using immunohistochemistry.
Results and discussion. In placenta accreta, EPO expression in placental villous-stromal macrophages was statistically significantly higher than in the control group. Furthermore, in placenta accreta, a clear trend toward an increase in the number of syncytiotrophoblast cells positively expressing EPO was recorded. In abnormal placental attachment (especially in placenta accreta), ghrelin expression in symplastotrophoblast cells was statistically significantly higher than that in the control group. The number of villous-stromal macrophages expressing ghrelin in PAS significantly exceeded that in placenta previa and its normal location. Placental expression of ghrelin and erythropoietin in the amniotic epithelium and decidual cells did not differ between the groups.
Conclusions. In placenta accreta, erythropoietin and ghrelin expression in villous-stromal macrophages was statistically significantly higher than in normal placentation. In placenta accreta, a clear trend toward increased erythropoietin and ghrelin expression in the symplastotrophoblast was recorded. We propose the use of serum erythropoietin and ghrelin levels as promising serum biomarkers for placenta accreta.
Introduction. In the Russian Federation (RF), in 2021, the Ministry of Health of Russia approved the Regulations and Monitoring of Critical Obstetric Conditions (COC), which includes patients with COC in a specialized system and defines its role in obstetric practice.
Objective. To prove the effectiveness of early diagnosis and routing of critical obstetric conditions in reducing the maternal mortality rate from obstetric hemorrhage, preeclampsia, and septic complications (from COVID-19) in the western medical zone of the Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug — Yugra.
Materials and methods. At the first stage, a study of demographic indicators was conducted in the Russian Federation (RF), the Ural Federal District (UFD), and the Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug (KhMAO) over the past 10 years. At the second stage, a single-center retrospective comparative study of the medical records of women in a level 3 perinatal center (PC) was conducted. At the third stage, a study of the level of angiogenic growth factors in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy was conducted in the prospective analysis group to assess the prognosis of severe PE and determine the timing of delivery, taking into account the clinical manifestations of PE and the indicators of biochemical screening in the first trimester. Statistical analysis was performed using Statistiсa 10 (USA) and StatTech v. 2.8.4 (Stattech LLC, Russia, 2020).
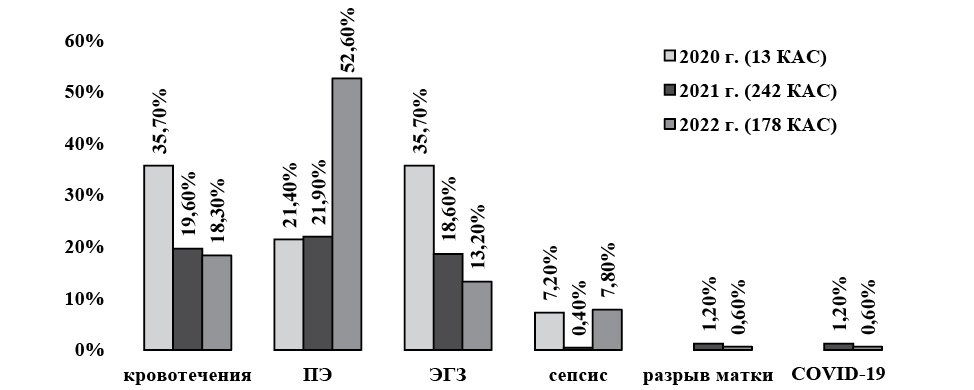
Study results. The structure of obstetric complications among pregnant women from healthcare facilities within the Khanty-Mansiysk Regional Clinical Hospital’s perinatal center’s area of responsibility in 2022 is presented in descending order: EGD, including diseases caused by SARS-CoV-2 infection (48.0%), preeclampsia (31.3 %), obstetric hemorrhage (11.2 %), and septic complications (7.8 %). Moreover, over the past decade, there has been an increase in the number of pregnant women classified as obstetric complications and referred for delivery to the Khanty-Mansiysk Perinatal Center, which has made it possible to avoid maternal losses, including those from COVID-19 and its complications, over the past 9 years. At the same time, the number of births, as elsewhere in the Ural Federal District and the Russian Federation, is declining: by 31.1 % over the past 10 years. According to data from the western medical zone of the Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug, the survival rate was 100 %, and the mortality rate was zero, including from SARS-CoV-2 infection and its complications.
Conclusion. The existing resources of the perinatal center at the Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug Multidisciplinary Hospital, despite the increasing age of reproductive function of patients and the number of pregnant women with comorbid pathologies, allow for more effective provision of specialized medical care. A multidisciplinary approach to assessing the severity of CAS patients, including those with SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus infection, has prevented fatal maternal outcomes in patients in the assigned area.