EDITORIAL
Endometriosis is a chronic multifactorial disease that affects more than 170 million women of reproductive age worldwide, causing pelvic pain syndrome, dyspareunia, and symptoms of gastrointestinal dyspepsia, thereby having a negative impact on the psycho-emotional state of patients. Despite a wide range of medical and surgical treatments, the relapse rate reaches 50%, which is a global economic and social problem.
The purpose of the study. to evaluate the mutual influence of clinical manifestations of intestinal disorders and the state of the intestinal microbiota in patients with deep endometriosis.
Materials and methods. The study included 83 patients of reproductive age who underwent surgical treatment of common forms of external genital endometriosis. The first group consisted of 32 patients of reproductive age who underwent repeated surgical treatment due to relapse of deep infiltrative endometriosis, the second group — 51 patients without relapse of the disease one year after the primary operation, due to deep infiltrative endometriosis, the third group — 30 patients of reproductive age. not suffering from external genital endometriosis. An analysis of the somatic anamnesis was carried out, as well as questionnaire data on pelvic pain on a visual analogue scale (VAS) and functional bowel disorders in patients with deep infiltrating endometriosis, depending on the status of relapse of the disease. The composition of the intestinal microbiota was assessed by quantitative real-time PCR using a test system for determining the DNA of intestinal-associated microorganisms.
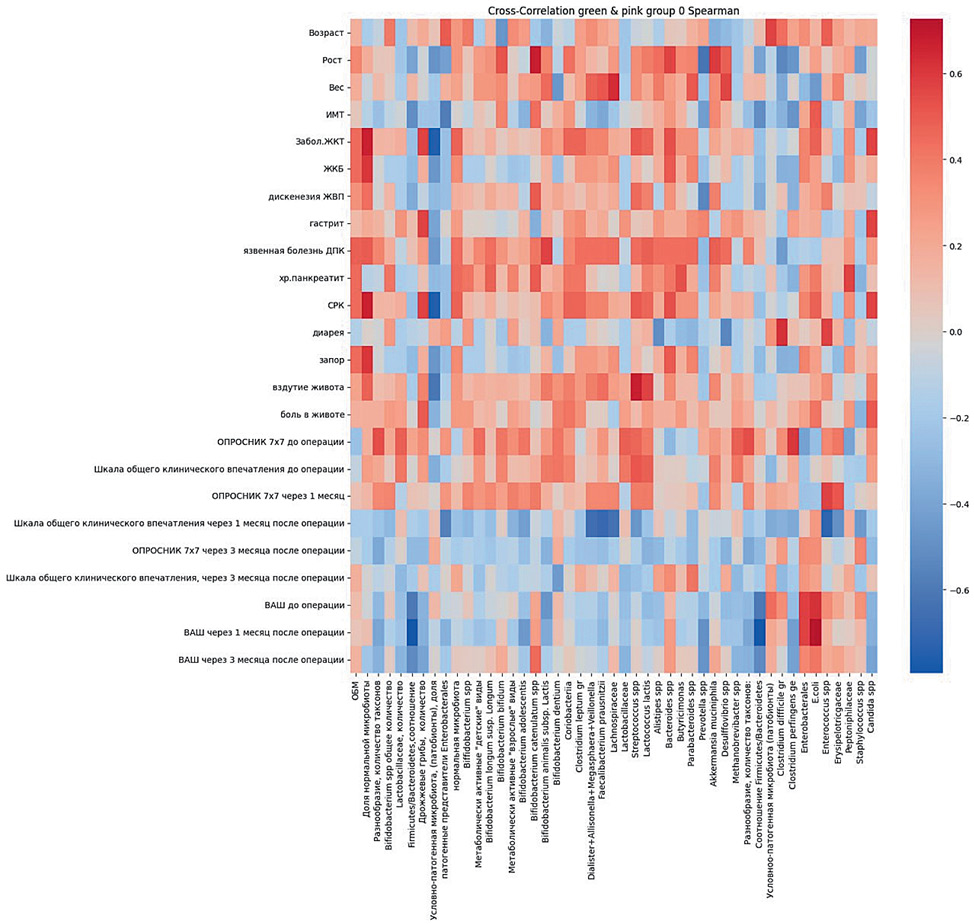
Results and discussion. The results of the study demonstrate bidirectional relationships between clinical and microbiological parameters and the recurrent course of deep endometriosis. Patients of the main group significantly more often suffered from functional diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, the spectrum of which was represented by chronic gastritis and irritable bowel syndrome. Correlation relationships between indicators of the Bacillota domain of the intestinal microbiota and clinical and anamnestic indicators of gastrointestinal pathology, the values of questionnaire scales in patients with deep endometriosis demonstrate moderate positive relationships between the weight of patients and the number of Lachnospiraceae (r = 0.63299), symptoms of bloating and the number Streptococcus spp (r=0.67402). Correlation relationships between indicators of the Bacteroidota domain of the intestinal microbiota and corresponding indicators demonstrate strong positive relationships between the amount of E.Coli in the intestinal microbiota and the level of pain assessed on the VAS scale after 1 (r = 0.62366) and 3 months (r = 0. 72598) after surgery. Moderate positive correlations were revealed between the number of Enterobacterales in the intestinal microbiota and the level of pain assessed on the VAS scale 1 (r=0.58169) and 3 months (r=0.57706) after surgery.
Conclusions. The recurrent course of endometriosis is accompanied by functional intestinal disorders, the manifestations of which persist after surgical treatment, which is mediated by changes in the intestinal microbiota. In patients with recurrent deep endometriosis, a decrease in the species and taxonomic diversity of the intestinal microbiota was found, due to an increase in the Bacillota/Bacteroidota ratio, the number of pathobionts, and a decrease in the number of commensal bacteria of the genus Bifidobacterium spp. These clinical and microbiological parallels demonstrate the need to harmonize the intestinal microbiota as a comprehensive prevention of disease relapse.
REVIEWS
Background. Pregnancy represents a unique immunological and physiological period during which microbial communities can have a significant impact on both maternal health and birth outcomes. Hormonal, immunological, and metabolic changes during pregnancy influence the microbiome and clinical outcomes, potentially impacting the well-being of both mother and child.
Objective: generalization of modern scientific concepts about the relationship between the composition of the mother’s microbiota during pregnancy and its complications, discussion of the possibility of predicting pregnancy complications using the microbiome.
Materials and methods. An extensive literature review was conducted using the MEDLINE (PubMed) database as of December 2024 with the following keywords and filter: randomized controlled trial, meta-analysis, systematic review.
Research results: Extensive research links the dominance of certain Lactobacillus strains to different pregnancy outcomes, with L. cripatus being the most favorable strain. Only by existing in a normal symbiotic relationship between the organism and the microbiome is it possible to maintain homeostasis. Any shift in the balance in this system leads to the growth of opportunistic flora, which in turn triggers a cascade of immunological and physiological disorders. GDM, PCOS, premature birth — these conditions have features of the vaginal microbiocenosis.
Conclusion. The microbiome composition of the female reproductive tract and intestine is dynamic during pregnancy and is influenced by a number of factors. More evidence suggests that dysbiosis is associated with various adverse pregnancy outcomes. Knowledge of the microbiome composition has the potential to improve the accuracy of diagnosis, develop targeted interventions, and reduce the risk of perinatal complications.
Background. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM) is a common disorder that is getting a special attention recently due to the unwanted outcomes that it leaves on the health of both the women and their offspring. New approaches are being applied in order to develop strategies that prevent GDM and its consequences on the metabolic and physiological state. One of the factors that have been thought to be involved in the pathology behind this disorder is the microbiome.
Objective: to determine the current evidence regarding the association of the maternal microbiota composition with gestational diabetes mellitus and to discuss the possibility of the management of GDM using the microbiome.
Material and methods. An extensive literature review was conducted using the MEDLINE database (PubMed) using keywords and filter: randomized controlled trial, meta-analysis, systematic review.
Research results. This review summarizes the main data on the influence of microbiota composition and diversity on the occurrence and development of GDM. Although there were some inconsistencies among the results, a pattern of significant changes in the gut, oral, and vaginal microbiome of women with GDM was observed. It was found that the composition and diversity of gut microbiota were significantly associated with the occurrence and development of GDM. Specifically, the abundance of certain gut bacteria is associated with anincreased risk of GDM, while other changes in the microbiome may beassociated with improved insulin sensitivity. In addition, alterations in the gutmicrobiota may affect blood glucose control through a variety of mechanisms, including the production of short-chain fatty acids, activation of inflammatory pathways, and metabolism of the B vitamin group.
Conclusion. We concluded a clear existing correlation between GDM and the microbial communities, where specific patterns of alterations in the microbiome was observed in the gut, oral and vaginal tracts of the pregnant women. These findings, although having some limitations, are promising and encouraging to develop strategies that target the human microbiome in order to develop novel therapeutic plans to treat or prevent GDM using next generation probiotics and parabiotics. Future studies should assess the outcomes and the efficacy of such therapeutic methods.
Background. According to world statistics, 7% of patients out of 100 in high-income countries and 15% of patients out of 100 in low- and middle-income countries develop infections related to medical care. As follows from the report of the World Health Organization, one in four cases of hospital sepsis that occurred in the intensive care unit is caused by hospital strains. On average, one in ten of these patients has a hospital-acquired infection that is fatal. The high-risk group includes patients in intensive care units, including newborns. In 2023, 28973 cases of neonatal infections (including intrauterine infection) were registered in medical organizations of the Russian Federation. The highest rates of neonatal morbidity were recorded in the Sverdlovsk Region (42.2%), the Trans-Baikal Territory (33.0%), the Novosibirsk Region (26.0%), the Chelyabinsk Region (22.4%), the Krasnoyarsk Territory (21.8%) and the Irkutsk Region (21.3%). Thus, infection prevention and control strategies aimed at both patients and their environment are of paramount importance in neonatal intensive care units.
Objective. To summarize current relevant data on the prevention of hospital infections in neonatal intensive care units.
Materials and methods. A literature review was conducted using the MEDLINE database (PubMed) as of December 2024 using keywords and a filter: randomized controlled trial, meta-analysis, systematic review.
Results. This review summarizes the main data on the prevention of hospital infections in neonatal intensive care units. According to the literature, ensuring bacteriological safety in relation to the development of hospital infections depends on many factors: hand hygiene of medical personnel, organization of venous access control, disinfection of medical equipment and premises, compliance with the rules of asepsis and antiseptics when performing invasive manipulations, the introduction of modern approaches in the care of premature infants.
Conclusion. There are many tasks in the intensive care unit that require innovative strategies to ensure the safe care of premature newborns. Joint efforts to standardize the processing of specialized equipment, maintain the cleanliness of the environment, comply with vascular access care protocols, adequate hand hygiene, and the active introduction of parents into newborn care are an integral part of the program aimed at preventing nosocomial infections. Active cooperation between the neonatal intensive care unit and the epidemiological service of the institution will allow us to develop a rational policy for risk management and monitoring of hospital infections.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Background. Fetal growth restriction (FGR) is a serious medical and social problem, which is associated with high perinatal morbidity and mortality, as well as long-term consequences for offspring. To date, there are no absolute instrumental tests for accurately predicting the condition of the fetus, which justifies the relevance of this study.
Objective. To study the features of the anamnesis, the course of pregnancy, and the outcome of childbirth in women with fetal growth restriction.
Materials and methods. A retrospective cohort study was conducted using a continuous sample of 200 women who were delivered at the Clinic of the South Ural State Medical University (Chelyabinsk) in 2022. All the women were divided into two groups: group 1 - 30 women with FGR, group 2 - 170 women without FGR. The outcomes of pregnancy and childbirth were studied (the results were obtained by means of a questionnaire, analysis of medical documentation: the book of a pregnant woman, the history of childbirth).
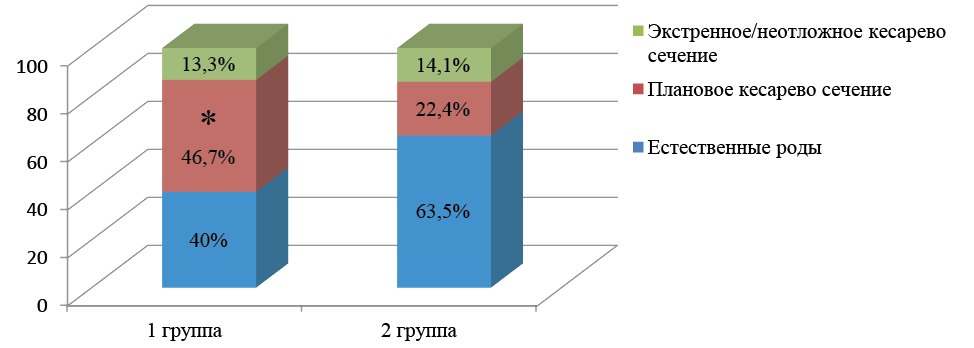
Results. There was a low effectiveness of the prognosis of FGR both according to the results of the analysis of anamnestic risk factors and according to laboratory and instrumental screening programs at 11-13,6 weeks of gestation. A low percentage of coverage with drug prevention was registered in the high-risk group of FGR (55%). We found that FGR is associated with other placental disorders, which more often began in the second trimester with changes in uterine and fetal blood flow and progressed as the gestation period increased. Fetal growth restriction is associated with severe preeclampsia, high incidence of premature birth, cesarean section, hypotrophy and severe asphyxia of newborns.
Conclusion. The absence of significant anamnestic risk factors, the low effectiveness of predicting fetal growth retardation based on the results of programmatic screening at 11-13,6 weeks require the development of new modern methods for predicting pathology. Research should focus on the development of new fetal diagnostic tools that can improve the accuracy of predicting critical fetal conditions, as well as on the introduction of innovative therapeutic measures aimed at improving placental hemodynamics, which will further optimize the timing of delivery.
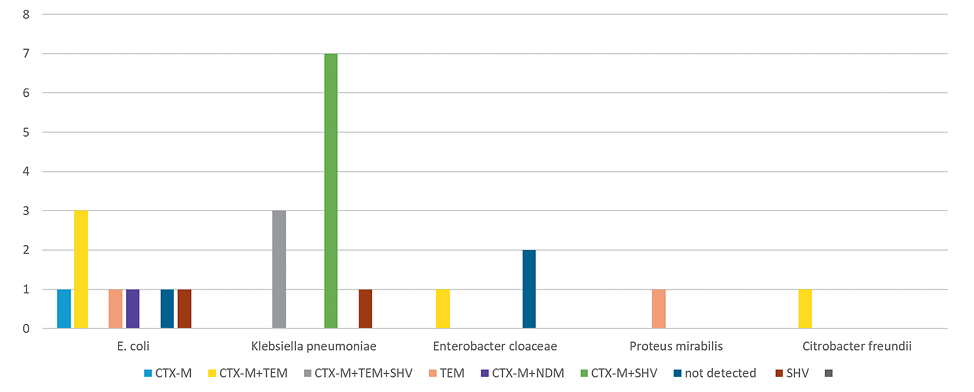
Background. Antibiotic resistance of microorganisms is a significant problem for public health in countries around the world. Studying the structure and prevalence of genetic determinants of antibiotic resistance is a current research area that makes it possible to determine the mechanisms of resistance to antibacterial drugs.
Purpose of the study. To study the genetic profile of antibiotic resistance of Enterobacteriaceae strains isolated from obstetrics, gynecology and pediatric patients.
Materials and methods. The genetic profile of antibiotic resistance was determined in ESBL-producing strains of Enterobacteriaceae isolated from samples of biological material obtained from 43 women and 24 children hospitalized in the departments of the Federal State Budgetary Institution “Research Institute of OMM” of the Russian Ministry of Health in 2024. The DNA of bacterial cells of ESBL-producing isolates was isolated from a daily culture of microorganisms using the PROBA-NK kit. Detection of genes blatem, blactx-M-1, blashv; blaoxa-40-like, blaoxa-48-like, blaоxa-23-like, blaoxa-51-like, blaimp, blaKPS, blaNDM, were carried out using the BakResist GLA kit on a DT-48 detection amplifier (DNA technology, Russia ).
Results. In representatives of the Enterobacteriaceae family isolated from children, the blactx-M-1+blashv genovariant was identified in 29.2% of cases and was found only in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Blatem+blactx-M-1 was detected in 20.8%, and blactx-M-1+blashv+blatem — in 12%. Among representatives of the Enterobacteriaceae family isolated from women, the blactx-M-1 genovariant was found in 37.2% of cases and was detected only in Escherichia coli. And the options blactx-M-1+blatem and blactx-M-1+blashv — in 16.3%. In 2024, for the first time in 7 years of our research to identify the genetic determinants of antibiotic resistance, a multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli strain with the blaNDM gene was identified. Also noteworthy is the identification of K. pneumoniae with the genetic profile of antibiotic resistance blatem, blactx-M-1, blashv, blaoxa-48-like, blaNDM.
Conclusion. The genetic profile of antibiotic resistance of Enterobacteriaceae strains isolated from patients in obstetrics, gynecology and pediatric departments is represented by 8 genovariants, in which the dominant gene providing resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics among Enterobacteriaceae in 2024, as in 2021, 2022, blaCTX-M-1 remains, which is found both as a monovariant and in association with blatem and blashv.
Background. Group B streptococcus (Streptococcus agalactiae, SGV) remains the main cause of neonatal sepsis and meningitis, despite a marked decrease due to the use of intranatal antibiotic prophylaxis. At the same time, delays in the detection and treatment of neonatal infections can cause serious consequences and, in some cases, the death of a newborn, on the other hand, unnecessary use of antibiotics also has harmful consequences (changes in the normal microbiota of a newborn, the development of antimicrobial resistance, etc.). At the same time, laboratories are constantly faced with the task of improving diagnostic approaches for the rapid and correct identification of newborns with infection.
The purpose of the study. To analyze the effectiveness, efficiency and timing of the results of bacteriological examination in neonatal sepsis and meningitis caused by Streptococcus agalactiae to determine the best diagnostic strategy.
Material and methods. In the period from January to November 2024, the case histories of 10 newborns with positive hemoculture for Streptococcus agalactiae were analyzed. Blood samples were taken under aseptic conditions according to the standard protocol. The identification of microorganisms was carried out by 2 methods: 1 — by standard subcultivation on nutrient cups and 2 — directly from positive vials using MALDI-TOF MS technology on a Vitek MS analyzer (BioMerieux, France) using the in-house method.
Results. The average time from the moment of sampling to placement in the hemocultivation device (A) was 13.1±7.4 hours, the average growth time of the microorganism, i.e., to a positive signal (B) was 6.7± 3.0, the average time for identification of the pathogen from a blood vial (C) was 20.2±13.1, the average sample turnover time in the laboratory (from the collection of the material to the issuance of the identification result to the clinician — D) was 42.0 ± 12.0 hours. When using the accelerated identification method directly from a positive vial, the average time C was 12.5 hours, D — 36.3 hours.
Conclusions. The use of an accelerated technique for the cultural detection of OHS in hemocultures of newborn children allowed to reduce the time of identification of the pathogen in a positive blood culture by 17.5 hours from 30 hours to 12.5 (more than 2 times), and the total time from obtaining the biomaterial to making a decision by the attending physician was reduced by 14 hours (from 50 hours to 36), i.e. almost 1.5 times.
Introduction. Over the past decades, outstanding progress has been made in caring for extremely premature infants and newborns with severe pathologies. Management of this vulnerable category of patients is associated with the continued risk of developing infectious pathology. In the structure of nosological forms, neonatal sepsis caused by coagulase-negative staphylococci occupies one of the leading positions. There is an increase in the number of antibiotic-resistant strains, including among Staphylococcus epidermidis, a typical representative of the normal microbiocenosis of human skin, so colonization of a premature newborn child who is at the stationary stage of nursing with it is a typical process.
Objective. To study changes in the minimum inhibitory concentration of antibacterial drugs for Staphylococcus epidermidis strains isolated from the contents of the tracheobronchial tree of newborn children at the nursing stage in a hospital setting.
Material and methods. To assess the statistical significance of the results obtained, the Chisquare test with Yates correction and the Mann-Whitney U test were used. Research results. All strains tested were resistant to cefoxitin. This, in turn, determines resistance to protected penicillins, amoxicillin clavulanate, ampicillin, sulbactam, and cephalosporins of I-IV generations. 44.4% and 87.5% of Staphylococcus epidermidis strains resistant to gentamicin were registered in 2022 and 87.5% in 2024.When comparing the MIC to gentamicin of Staphylococcus epidermidis isolated from TBD, a significant increase in indicators was established in 2024 compared to 2022 (Mann-Whitney U test is 7.5; p<0.05). The proportion of clindamycin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis strains is 44.4% in 2022 and 12.5% in 2024 (p = 0.179). > < 0.05). The proportion of clindamycin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis strains is 44.4% in 2022 and 12.5% in 2024 (p = 0.179).
Conclusion. Thus, the analysis of antibiotic resistance of staphylococci isolated during bacteriological examination of the contents of the tracheobronchial tree demonstrates an increase in the MIC of Staphylococcus epidermidis to gentamicin.The high therapeutic potential of vancomycin, a deep reserve antibiotic for the treatment of congenital and hospital-acquired pneumonia in premature newborns, remains high.
Background. The introduction of new technologies into the process of medical rehabilitation is relevant today, since modern healthcare faces the most important tasks to increase the life expectancy of citizens, reduce the level of disability of the population, and great attention is paid to rehabilitation after diseases (including combating the consequences of coronavirus infection) in order to ensure the restoration of health and improve the quality of life of patients.
Objective. To analyze changes in the work of a medical rehabilitation institution in the process of upgrading equipment within the framework of the federal project “Optimal medical rehabilitation for health restoration”.
Materials and methods. The material was the data of the annual report of the State Medical Institution SO “OSBMR Lipovka”. Statistical and analytical research methods were used. The statistical analysis was carried out using the StatTech v. program. 4.1.2.
Results. The number of patients treated in 2023 increased significantly compared to previous years (+27% to the level of 2022 and +20% to the level of 2019). In 2023, there was a significant increase in the number of procedures performed (+30% compared to the level of 2022 and +42% compared to the level of 2019) due to the arrival of new equipment within the framework of the federal project “Optimal medical rehabilitation for health restoration”.
Conclusion. The introduction of new equipment obtained within the framework of the Federal project “Optimal medical rehabilitation for health restoration” allowed to increase the number of hospitalizations of patients, significantly increased the number of procedures per patient.