EDITORIAL
According to WHO, cardiometabolic disorders have remained the leading cause of death in the world for 20 years. Heart diseases account for 16% of deaths worldwide today, reaching 47% in Russia. Unfortunately, awareness of CVD as a leading cause of death remains insufficient among both women and physicians. The risk of CVD in middle-aged women remains underestimated and certainly requires timely interdisciplinary attention. The aim of the study was to conduct a literature review of databases in the context of studying the problem of cardiovascular risk realization in peri and postmenopausal women. Research methods. An analysis of evidence published in 2015-2025 in the Cochrane Library, PubMed, ELibrary, Science Direct, Scopus, Web of Science, Google Scholar electronic libraries was conducted using the keywords cardiovascular diseases, cardiovascular risk, peri and postmenopause, menopausal hormone therapy. Results of the study. The review presents the main determinants of the implementation of cardiometabolic and cardiovascular risks in women in peri and postmenopause both in terms of aging and in terms of the influence of menopausal hormone therapy. Conclusion. The presented data convincingly indicate that in order to prevent the implementation of cardiovascular risk in women in peri and postmenopause, it is necessary to create a personalized pathogenetically substantiated strategy of therapeutic and preventive measures based on the concept of preventive medicine.
REVIEWS
Pelvic organ prolapse (POP) is a common condition affecting women of all ages. Undoubtedly, surgical treatment of symptomatic pelvic floor prolapse should combine reliable restoration of anatomical structures, pelvic floor functions and high efficiency in the long term. The recurrence rate of pelvic organ prolapse after surgical treatment is still high and can be up to 50%, while 30% of patients will require repeated surgical treatment. The reasons for the unsatisfactory result of surgical restoration of the pelvic floor are still unknown. Some authors are inclined to the hypothesis that the recurrence of POP occurs due to impaired tissue regeneration. It is necessary to use techniques aimed at improving regenerative activity in the perioperative period to improve the outcome of surgical inter ventions on the pelvic floor. The aim of the study. To analyze the methods of preoperative preparation of patients with pelvic organ prolapse. Study design. An analysis of evidence was conducted that was published in 2015-2025 in the electronic libraries Cochrane Library, PubMed, ELibrary, Science Direct, Scopus, Web of Science, Google Scholar, using the keywords pelvic organ prolapse / pelvic organ prolapse, preoperative preparation / preoperative preparation. Results of the study. Tissue regeneration includes several phases: hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation and remodeling. Impact on these phases helps to improve the outcomes of surgical treatment. Pelvic floor muscle training has not shown its effectiveness as a perioperative intervention. Local application of estrogens, often in combined forms, in postmenopausal women, according to the literature, shows good results as a preoperative preparation based on subjective data, histological examination and postoperative recurrence. Women of reproductive age should receive minimally invasive preoperative preparation aimed at improving the anatomical and functional result. Patients with severe tissue trophism (decubital ulcers) need complex multicomponent preparation for surgical treatment.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
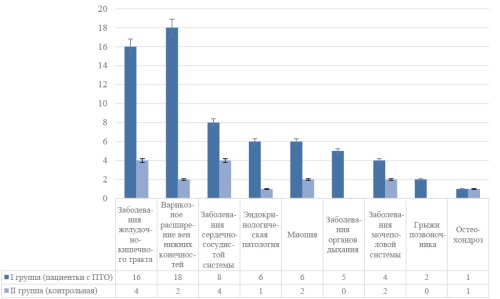
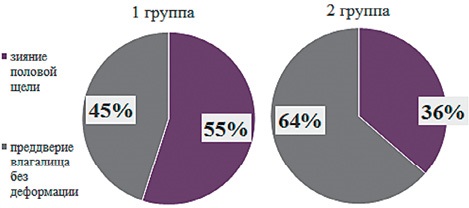
Pelvic organ prolapse (POP) is a pressing medical and social problem that significantly affects the quality of life of women of reproductive age. According to epidemiological studies, the incidence of this pathology in women under 40 years reaches 15-20%, while there is a tendency for POP to become younger. However, other pelvic floor disorders, such as urinary incontinence and sexual dysfunction, are often ignored. All these pathologies are combined into pelvic descent syndrome (PDS). Research into risk factors for PDS development and identification of target groups is necessary for early diagnosis and successful treatment. The aim of the study. To evaluate clinical and anamnestic risk factors for the development of pelvic floor syndrome degradation in women of reproductive age. Study design. A prospective study was conducted. a cohort study that included 88 women of reproductive age (18-49 years). The patients were divided into 2 groups: Group I — women with pelvic descent syndrome (n=58), Group II — control (n=30). Within the framework of this study, an assessment of anthropometric parameters, obstetric and gynecological history and concomitant somatic diseases was carried out. To assess sexual function, was used validated self-administered questionnaire “Female Sexual Function Index” (The Female Sexual Function Index, FSFI). The function of the urinary tract was studied using uroflowmetry. The study was conducted on the TRITON urodynamic system (Laborie Medical Technologies, Canada). Research results. Significant clinical and anamnestic predictors of pelvic descent syndrome are the number of pregnancies more than three, the number of births more than two, the presence of perineal injuries during childbirth, childbirth with a large fetus, obesity. Patients with pelvic descent syndrome have pronounced sexual dysfunction, but do not actively complain about the quality of sexual life.
Background. Pelvic organ prolapse, urinary and fecal incontinence and sexual dysfunction are collectively termed “pelvic floor dysfunction”, the main causes of which are pregnancy and childbirth, which leads to decreased pelvic floor muscle strength and increased frequency of urinary incontinence. Studies show that stress urinary incontinence during pregnancy occurs in a significant proportion of women, and these problems may persist and progress in the postpartum period, especially in those who have suffered injuries during childbirth. In addition, women with complications during pregnancy and childbirth experience more pronounced manifestations of sexual dysfunction and delayed resumption of sexual activity. All these factors indicate the need for early screening and diagnosis of pelvic floor dysfunction in women during pregnancy to improve quality of life and prevent subsequent complications. Objective. To identify predictive ultrasound markers of pelvic floor dysfunction in primiparous women after per vias naturales delivery at the antenatal stage. Material and methods. A prospective cohort comparative study was conducted among 40 women of reproductive age before delivery and 6-8 weeks after delivery per vias naturales in occipital presentation of the fetus. The main group consisted of 18 women who still had symptoms of pelvic floor dysfunction at the end of the late postpartum period; the control group included 22 women without clinical manifestations. All patients underwent a gynecological examination with perineometry and ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs before delivery and 6-8 weeks after delivery. Results. In the group of women who had clinical manifestations of pelvic floor dysfunction, a decrease in pelvic floor muscle tone was noted 6-8 weeks after delivery. These women of ten reported urinary disorders, including frequent urination and stress urinary incontinence. During the instrumental study, it was revealed that already in the third trimester of pregnancy, changes in the urethrovesical angle occurred according to ultrasound examination data, and a decrease in the size of the perineal tendon center and a change in the parameters of the thickness of the bulbospongiosus muscle bundles were observed. Conclusion. Non-invasive diagnostic methods can identify the risks of pelvic floor insufficiency even during pregnancy, which will subsequently allow timely treatment of pelvic dysfunctions in women of reproductive age. Active identification of such patients will help reduce the number of surgical interventions and improve the quality of life of women of reproductive age.
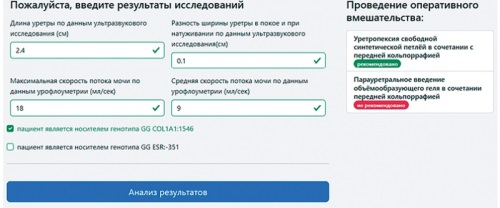
Background. Stress urinary incontinence in postmenopausal women is one of the urgent problems of modern urogynecology. According to WHO, about 160 million women world wide suffer from this pathology. The existing modern methods of urinary incontinence correction are aimed at improving the support of the vesico-urethral junction and correcting insufficient closure of the urethra. However, currently there are no tools to determine which of the options for the operation to perform in each specific case. The purpose of the study. To develop software for choosing a method of surgical treatment of stress urinary incontinence in combination with cystocele in postmenopausal women based on a comprehensive preoperative examination. Material and methods. A prospective randomized study was conducted, which included 80 postmenopausal women with stress urinary incontinence in combination with cystocele, who were admitted to the gynecological clinic of the Federal State Budgetary Institution Research Institute of OMM for surgical treatment. All patients, after signing a voluntary in formed consent to participate in the study and conducting a comprehensive preoperative examination using a random number generator, were randomized into two groups. The first group (group A) consisted of 40 women who received surgical treatment in the amount of anterior colporrhaphy in combination with urethropexy with a synthetic loop; the second group (group B) included 40 patients who underwent surgical treatment by the method of paraurethral injection of a volume-forming gel in combination with anterior colporrhaphy. Static data processing was carried out using the application package Excel, SPP Statistics 22.0, Statistica for Windows 10 (TIBCO Software Inc., Palo Alto, CA, USA).For scores with a normal distribution, the mean and standard deviation were reported. Testing of statistical hypotheses about the absence of intergroup differences for quantitative traits with a normal distribution was carried out using Student’s t-test. For dichotomous indicators, the relative value as a percentage were indicated, and the chi-square test was used to test statistical hypotheses. Research results. The developed formulas and the created software allow the clinician to choose the method of effective surgical treatment of SUI in combination with cystocele in postmenopausal women, thereby implementing a personalized approach to choosing the method of surgical treatment. Conclusion. Thanks to the developed formulas and the creation of software that could help the clinician to choose a method for effective surgical treatment of SUI in combination with cystocele in postmenopausal women, a personalized approach to choosing a method of surgical treatment has been optimized.
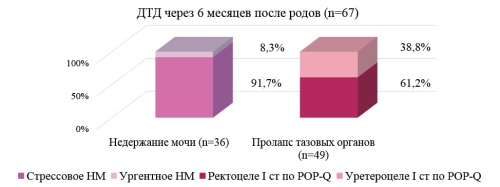
Background. during pregnancy and the postpartum period, anatomical and physiological changes in the structures of the pelvic floor occur. The most significant reorganization during pregnancy is undergone by connective tissue, the transformation of which is adaptive and adaptive in nature. Symptoms of pelvic organ prolapse, urinary incontinence, sexual dysfunction first begin to appear or progress, as a rule, after the first birth. In the modern world, women pay close attention to maintaining an active and fulfilling life after childbirth. The creation of a personalized approach to the prevention of pelvic floor dysfunction symptoms in women after childbirth, including highly effective rehabilitation measures, will improve the quality of all areas of life. The purpose of the study. to reduce the incidence of pelvic dysfunctions and urodynamic disorders based on the developed algorithm for monitoring women after childbirth and implementing rehabilitation measures. Material and methods. A two-stage prospective comparative study was conducted, which included 200 women after natural childbirth. At the first stage of the study, clinical and anamnestic predictors and instrumental markers of the development of pelvic and urodynamic dysfunctions were determined in 120 women after childbirth. Group A included 67 women who developed pelvic dysfunctions and urodynamic disorders, such as pelvic organ prolapse and urinary incontinence. Group B included 53 patients who were not found to have this pathology. A model for predicting the development of pelvic dysfunctions and urodynamic disorders in women after childbirth was created using logistic analysis methods based on clinical and anamnestic data and instrumental markers of the development of pelvic and urodynamic dysfunctions obtained at the first visit. At the second stage of the study, the clinical significance of the predictive model for the development of the risk of pelvic dysfunctions and urodynamic disorders after childbirth was tested, as well as rehabilitation measures were assessed in terms of their prevention. The examination sample of the second stage consisted of 80 women after natural childbirth. A high risk of developing pelvic dysfunctions and urodynamic disorders after childbirth was detected in 50 women, and a low risk was found in 30 women. Using a random number generator, high-risk patients were divided into two groups. Patients in group B (n=25) underwent a course of dynamic quadripolar radiofrequency (DQRF). Women in Group G (n=25) performed only home pelvic floor muscle training using individual portable Smart trainers. Women in Group D (n=30) were given general recommendations on lifestyle and recovery after childbirth. Research results. Prognostic markers for the development of pelvic dysfunctions and urodynamic disorders after childbirth were determined. Conducting rehabilitation measures presented in the form of a course of dynamic quadripolar radiofrequency reduces the incidence of pelvic organ prolapse and urinary incontinence 6 months after childbirth. Conclusion. For patients belonging to the high-risk group after childbirth, an algorithm has been developed to reduce the incidence of pelvic dysfunctions and urodynamic disorders 6 months after childbirth.
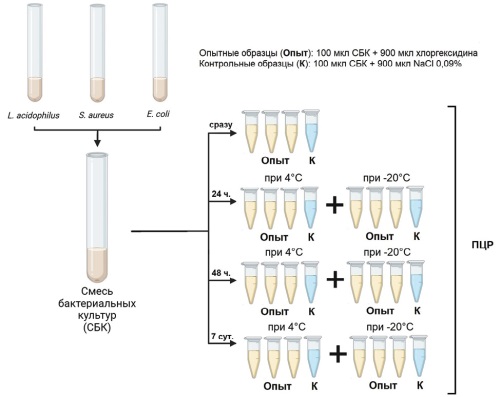
Introduction. A 0.05% solution of chlorhexidine digluconate (CD) is one of the most commonly used antiseptics, however it is unclear whether CD has an inhibitory effect on nucleicacid amplification during polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The aim of the study. To evaluate the impact of chlorhexidine digluconate on bacterial DNA preservation and PCR efficiency. Materials and methods. The susceptibility of Lactobacillus acidophilus, Staphylococcus aureus, and Escherichia coli mixture to 0.05% CD solution was studied after 1, 2, and 7-day of exposure in a refrigerator and freezer. Results. The CD solution did not cause PCR inhibition or destruction of bacterial DNA of any tested bacterial groups after 1, 2, or 7 days of exposure under the refrigerator and freezer conditions. Conclusions. The results obtained allow to interpret PCR tests for bacterial infections and the microbiota composition in a regular way, even after pretreatment of the mucosa with a 0.05% chlorhexidine digluconate solution.